Handle the Hassles of the Helium Shortage
Convert to alternative carrier gas

Convert to an alternative carrier gas
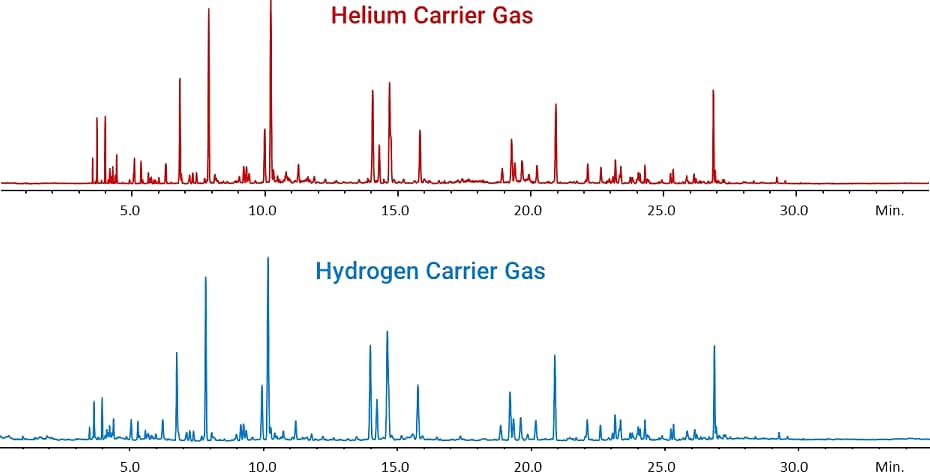
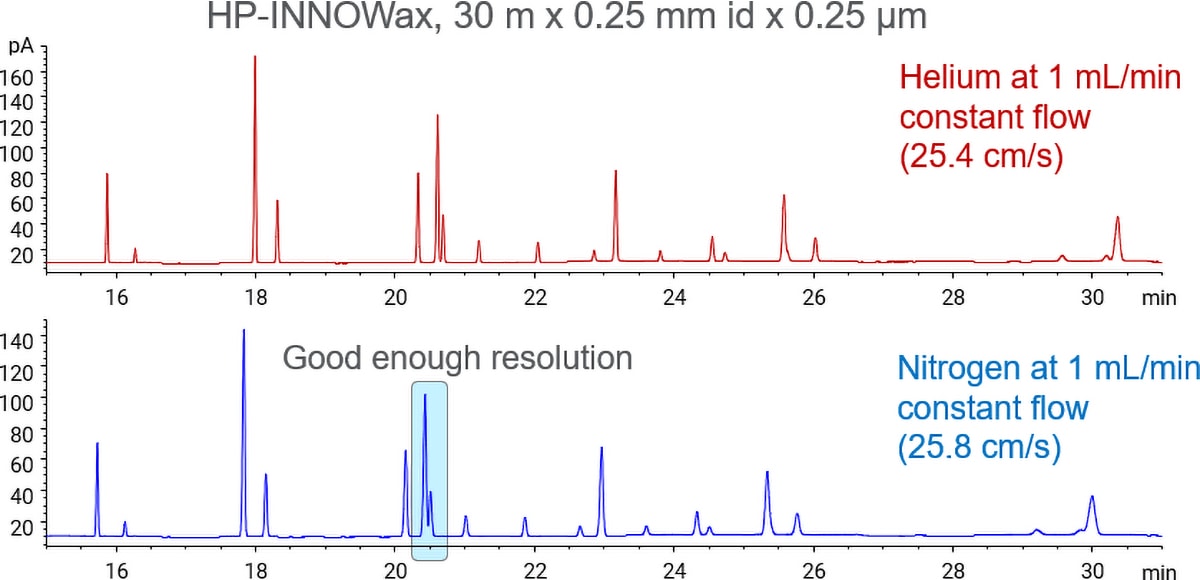
To avoid disruptions caused by helium shortages, consider an alternative carrier gas for your analyses. Hydrogen is a good option if you are using GC/MS, or if your method is resolution-critical. If you are performing GC, and if your method resolution is more than sufficient, try nitrogen.
Make sure that your system is compatible with an alternative carrier gas
This table will help you determine if your instrument configuration is compatible with hydrogen or nitrogen carrier gas. All components of your system—including sample introduction devices—must be able to use any alternative carrier gas you may be considering for your application.
System compatibility
| Technique | Product | Hydrogen Carrier Gas | Nitrogen Carrier Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC | 8890 GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) |
| Intuvo 9000 GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| 8860 GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| 8850 GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| 990 Micro GC | Yes | Yes | |
| 490 Micro GC | Yes | Yes | |
| 7890 Series GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| 7820 Series GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| 6890 Series GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| 6850 GC | Yes (all inlets) | Yes (all inlets) | |
| GC Detectors | FID | Yes (capillary columns) | Yes (capillary and packed columns) |
| TCD | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | Yes (capillary and packed columns)* | |
| ECD | Yes (capillary columns) | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | |
| NPD | No | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | |
| FPD | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | |
| SCD | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | |
| NCD | Yes (capillary and packed columns) | No | |
| GC/MS | 5977 Series single quad | Yes | Not recommended |
| 7000 Series triple quad | Yes | Not recommended | |
| 7010 Series triple quad | Yes | Not recommended | |
| 7250 Q-TOF | No | Not recommended | |
| 7200 Series Q-TOF | No | Not recommended | |
| 5975 Series single quad | Yes | Not recommended | |
| 5973 Series single quad | Yes | Not recommended | |
| Sample introduction | |||
| Headspace | 8697 Series | Yes | Yes |
| 7697A Series | Yes | Yes | |
| G1888 | No | Yes | |
| 7694 | No | Yes | |
| Thermal Desorption | TD-xr | Yes (multi-gas version) | Yes (all versions) |
| Purge and Trap | Lumin | Yes (must use inert gas for purge) | Yes |
| AQUATek | Yes (must use inert gas for purge) | Yes | |
| AtomX | Yes (must use inert gas for purge) | Yes | |
| * Typically only used when measuring helium or hydrogen in a sample. Information in this table is current as of April 24, 2024. |
|||
Compare carrier gas options
Carefully consider all your options when choosing a carrier gas for your GC or GC/MS method.
Pros and cons of each carrier gas
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Helium Carrier Gas | Always the first choice, if available | Frequent shortages and delivery interruptions |
| Excellent chromatographic and MS performance | Inconsistent or high costs | |
| All reference spectra in libraries are obtained with helium | Sometimes difficult to find in chromatographic grades | |
| Hydrogen Carrier Gas | Best alternative to helium | Requires attention to safety |
| Better chromatographic resolution and speed compared to helium | Requires attention to reactivity | |
| Nitrogen Carrier Gas | Inexpensive | Requires longer run times to achieve resolution |
| Widely available in chromatographic grades | Not recommended for use with MSD | |
| Safer than hydrogen |
Method translation for your alternative carrier gas
Agilent method translator software can help you convert from helium to hydrogen or nitrogen carrier gas. Using your existing helium method parameters, this tool will automatically suggest new pressure, flow, velocity, and temperature program rates for hydrogen or nitrogen carrier gas—ensuring virtually identical relative retention order.
Method translator is built into OpenLab CDS software, or it can be downloaded as a standalone application.