工作原理
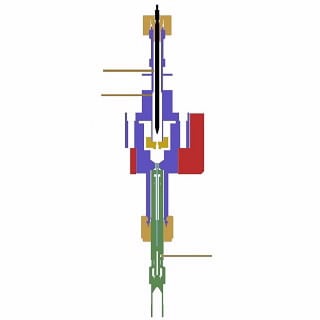
ECD 使用置于氮气或氩气-甲烷载气/补偿气气流中的低水平 β 发射器,通常为 63Ni。从放射源发射出的电子与补偿气气体分子碰撞,产生更多自由电子,这些电子被加速冲向用变频恒流电压极化的阳极。当样品进入检测器时,亲电化合物捕获电子,阳极电压频率增加以保持电流恒定。分析物浓度与电子捕获程度成正比。
有关产品介绍、应用和软件更新的直播或录播网络研讨会
仪器培训和讲座
气相色谱
微电子捕获检测器 (Micro ECD)
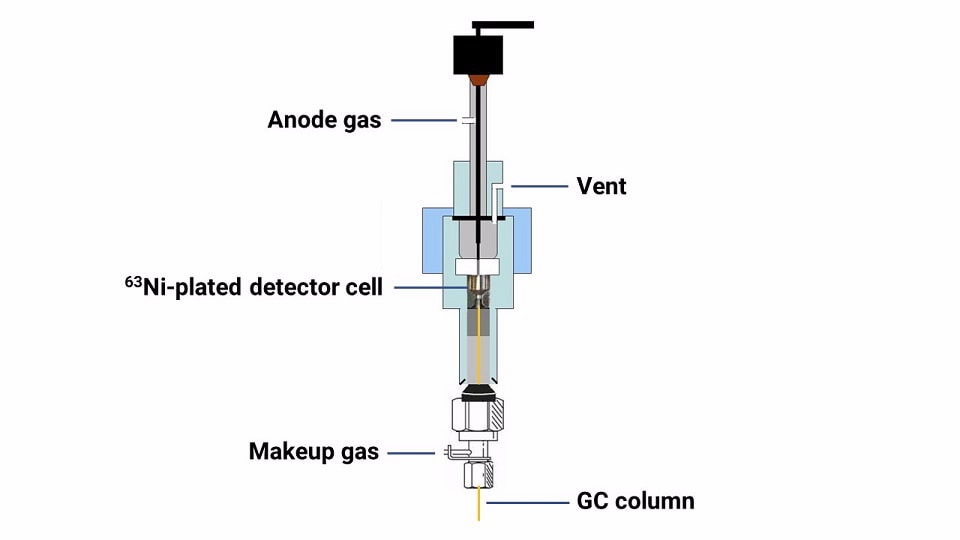
ECD 使用置于氮气或氩气-甲烷载气/补偿气气流中的低水平 β 发射器,通常为 63Ni。从放射源发射出的电子与补偿气气体分子碰撞,产生更多自由电子,这些电子被加速冲向用变频恒流电压极化的阳极。当样品进入检测器时,亲电化合物捕获电子,阳极电压频率增加以保持电流恒定。分析物浓度与电子捕获程度成正比。
This application note shows the analysis of halogenated hydrocarbons, and benzene and its derivatives in drinking water per GB/T 5750.8-2022 using the Agilent 8697 headspace sampler and Agilent 8890 GC.
Analysis of Flavor Compounds in Beer using 8697 headspace and 8890GC.
This document describes how to dispose of a used electron capture detector (ECD) when it is no longer needed or at the end of its operating life.
Highlights the features of and differences between GC detectors.
If you didn't find what you need, try these resources or contact a specialist
To access your Agilent account, please sign in again.
For your security, we will sign you out after 30 mins of inactivity.