Managing Director, AFIN-TS GmbH
Our SFC method development strategy always includes stationary phases of Agilent Technologies, Inc. We strongly appreciate the robustness of polar ZORBAX and Poroshell phases, such as ZORBAX Rx-SIL and Poroshell 120 HILIC. They exhibit good selectivity and high separation performance, which is key for successful and efficient method development in SFC. The broad spectrum of available column dimensions has great advantage for the optimization of separations and allows us to adjust the column dimension to obtain the most efficient separations.
View More
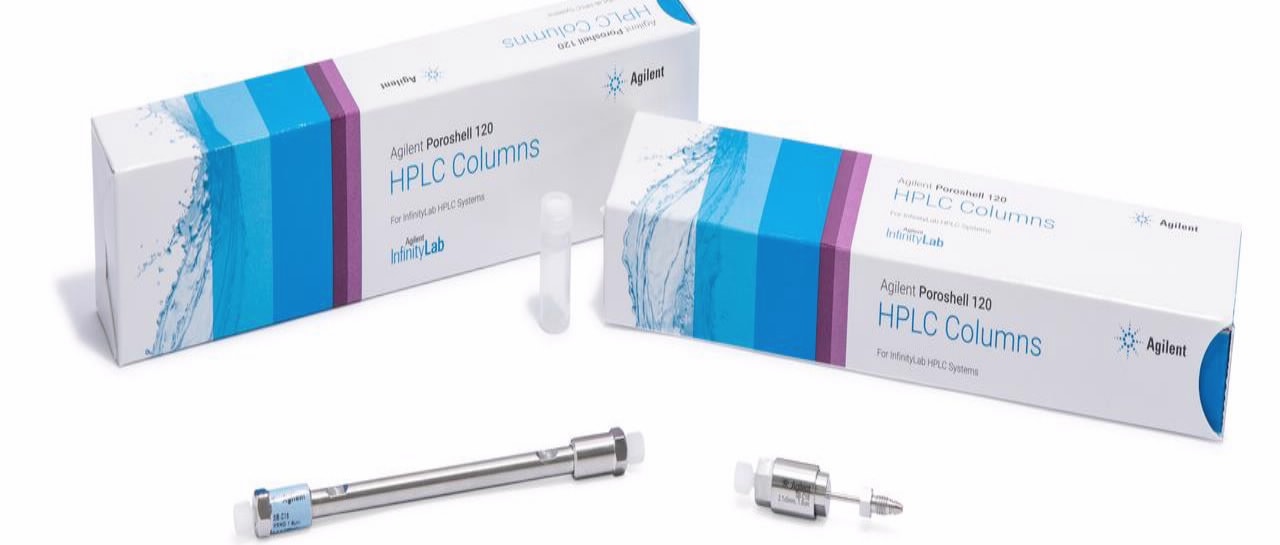
![Normal Phase/Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) Columns]()