Access Agilent eNewsletter November 2016

Agilent LC/MS/MS solutions provide effective identification and quantitation of contaminants in botanical drug supplements
Andreas Tei
Agilent Global Pharma Segment Manager
Thomas Glauner
Agilent Senior Application Scientist
More botanical drug products than ever before are being cultivated in large scale farming operations where agrochemicals are commonly in use. The routine screening and quantitation for hundreds of pesticides plays an important role in increasing final product safety. Additionally, contamination with noxious weeds or fungal infections has raised the importance of additional testing for other common contaminants, such as mycotoxins and pyrrolizidine alkaloids.
Use of modern orthogonal analytical technologies, such as liquid chromatography or gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry or ICP-OES/MS, are required to meet the latest standards from the United States Pharmacopeia (USP chapters <561> <563> <565>) and the European Medicines Agency Guidelines for botanical drug products. Advanced workflows and methodologies are needed to help to minimize safety concerns like a potential contamination with harmful residues, mycotoxins or heavy metals or an adulteration by the illegal addition of active pharmaceutical ingredients, dyes, and chemically synthesized active marker compounds to the original natural product.

Figure 1. Agilent 1290 Infinity II UHPLC coupled with a 6400 Series ion funnel triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
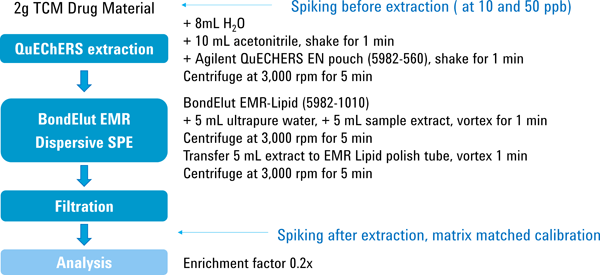
Figure 2. Schematics of the sample preparation workflow.
Figure 3. Reconstructed ion chromatograms displaying all acquired MRMs.
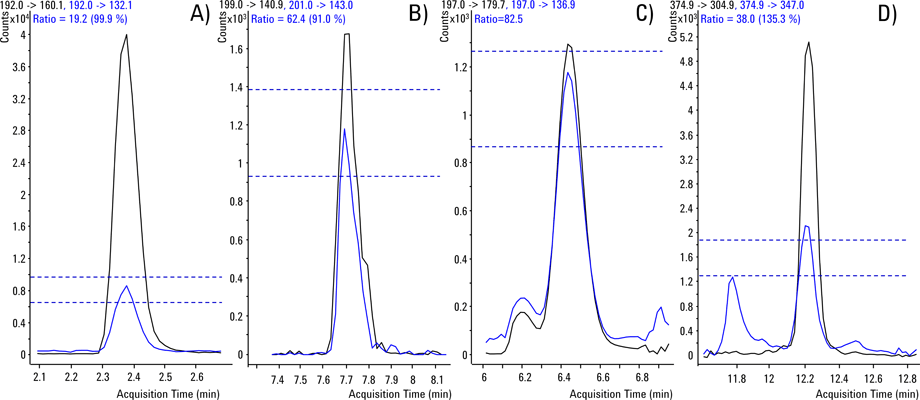
Figure 4. The ratios from qualifier and quantifier ions must be within the specifications to confirm the presence of compounds. The following pesticides have been detected in different samples: A) Carbendazim in Mor folium B) MCPA in Herba epimedii C) DNOC in Flos magnolia D) Profenofos in Cinamoni ramulus
Phytochemical fingerprinting of active marker compounds combined with the utilization of statistical programs like Principle-Component-Analysis, a tool from Agilent Mass Profiler Professional software, are very powerful in determining the authenticity of phytochemical drug products, which are frequently used in ethnic traditional medicines throughout China, Korea, Japan, other Asian countries, and India.
To demonstrate these techniques, ten different herbal drugs that are commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) were purchased from a pharmacy in Germany. We created a new workflow to screen and quantify common pesticides, mycotoxins and pyrrolizidine alkaloids in one analytical method. Herbal drug samples were analyzed using an Agilent 1290 Infinity UHPLC coupled to a highly sensitive Agilent 6400 Ion-Funnel triple quadrupole (QQQ) mass spectrometer, as shown in Figure 1.
Clean sample prep techniques facilitate accurate compound analysis
A key element of the workflow design is a modified QuEChERS extraction process and cleanup step using the Agilent Bond Elut Enhanced Matrix Removal Kit. Samples, each containing 2 g of plant material, were wetted with 8 mL of ultrapure water and were extracted according to the QuEChERS protocol using Agilent Bond Elut QuEChERS EN Kits. After QuEChERS extraction, lipids and similar matrix components were removed by a cleanup step using the Agilent Bond Elut Enhanced Matrix Removal Kit. A schematic of the workflow is shown in Figure 2. After filtration, the samples are ready to inject into an Agilent 1290 Infinity UHPLC system coupled to a highly sensitive Agilent 6400 series ion funnel triple quadrupole mass spectrometer using an Agilent 2.1 x 100 mm, 2.7 µ Poroshell 120 EC-C18 Column.
The LC/MS system was operated with dynamic MRM and in fast polarity switching mode. A reconstructed ion chromatogram displaying the acquired MRMs is shown in Figure 3. Two MRM transitions were acquired for each compound to identify and confirm the presence of a compound based on the chromatographic co-elution and a consistent ratio between the quantifier and the qualifier ion. Contaminants were only reported if the requirements of the SANTE guidelines were met (Figure 4).
Agilent QuEChERS and EMR cleanup combine to help meet SANTE guidelines
Recovery studies were made by spiking the plant materials with a comprehensive standard mix containing a total of 303 compounds (pesticides, mycotoxins, pyrrolizdine alkaloids) to concentrations corresponding to 10 µg/kg and 50 µg/kg. These samples were compared with extracts, which were spiked with the same standard mix, and to the same concentrations after extraction. With the generic QuEChERS extraction and EMR cleanup, more than 82% of the spiked compounds showed extraction recoveries of 70 to 120%, which is within the requirements of the SANTE guidelines.
Agilent LC/MS/MS solutions deliver effective contaminant detection
After investigating a very small sample number of ten different herbal drugs, we demonstrated that there are safety gaps regarding the drug products purity, as pesticides were detected in concentrations above the EU maximum residue level. Further orthogonal analytical technologies like GC/MS and ICP-MS are needed to obtain a more comprehensive overview of possible contaminants, in order to guarantee safety of botanical drug products. These results were published as a scientific poster for the 5th Annual Meeting of GP-TCM Research Association-cum-summit on Compendium of Materia Medica and Innovative Drug Discovery in Chinese Medicine. Contact your Agilent representative today to learn more.
Stay informed about the applications that are important to you
Subscribe to Access Agilent
Our free customized
monthly eNewsletter
Article Directory – November 2016
All articles in this issue
-
 Agilent 7010B and 7000D QQQ GC/MS systems expand your lab in multiple dimensions
Agilent 7010B and 7000D QQQ GC/MS systems expand your lab in multiple dimensions -
 Fast, accurate analysis of SVOCs with Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC
Fast, accurate analysis of SVOCs with Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC -
 Integrated workflow simplifies automated calculation of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR)
Integrated workflow simplifies automated calculation of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) -
 Tips & tricks:
Tips & tricks:
How to simplify troubleshooting in your GC lab using Agilent ADM Flow Meter -
 Agilent collaborates with BioPharma thought leaders in India to advance biosimilar characterization
Agilent collaborates with BioPharma thought leaders in India to advance biosimilar characterization -
 Achieve fast, high throughput size exclusion chromatography of mAbs and ADCs using Agilent AdvanceBio SEC columns
Achieve fast, high throughput size exclusion chromatography of mAbs and ADCs using Agilent AdvanceBio SEC columns -
 Ask the Expert: How can I analyze virtually any polymer, from paints to polyolefins?
Ask the Expert: How can I analyze virtually any polymer, from paints to polyolefins? -
 Agilent LC/MS/MS solutions provide effective identification and quantitation of contaminants in botanical drug supplements
Agilent LC/MS/MS solutions provide effective identification and quantitation of contaminants in botanical drug supplements -
 Agilent JetClean self-cleaning ion source means you clean less, analyze more
Agilent JetClean self-cleaning ion source means you clean less, analyze more -
 High-throughput N-linked glycan profiling of monoclonal antibodies using Agilent integrated solution
High-throughput N-linked glycan profiling of monoclonal antibodies using Agilent integrated solution
Figure 2

Schematics of the sample preparation workflow.
Figure 3

Reconstructed ion chromatograms displaying all acquired MRMs.
Figure 4

The ratios from qualifier and quantifier ions must be within the specifications to confirm the presence of compounds. The following pesticides have been detected in different samples: A) Carbendazim in Mor folium B) MCPA in Herba epimedii C) DNOC in Flos magnolia D) Profenofos in Cinamoni ramulus