Advancing Environmental Testing with Automated Cellular Insights
January 2026
Environmental testing has traditionally focused on chemical and biochemical assays to identify contaminants in water and other ecosystems. These methods remain essential, but they often lack biological context. To address this need, researchers are driving the adoption of automated, cell-based bioassay solutions. These approaches use living cells as sensitive indicators of stress and toxicity, complementing chemical analysis with biologically relevant insights. They also provide metabolic readouts of cellular responses, such as mitochondrial function and energy production, which are critical for understanding mechanisms of toxicity.
Agilent offers a unique suite of platforms and integrated solutions—including automated imaging systems, impedance-based real-time cell analysis, flow cytometry, and Seahorse XF metabolic analyzers—that enable robust quantitative analysis and support higher-throughput applications. These tools allow researchers to implement cell-based bioassays using 2D or 3D culture formats, whole-animal models like zebrafish, and other novel alternative methodologies (NAMs). Together, they deliver scalable, reproducible workflows for environmental testing, from real-time cytotoxicity profiling to advanced genotoxicity and mitochondrial assays.
Here we’ve compiled detailed resources to support the integration of these advanced bioassay approaches into your environmental testing workflows.
Featured Applications
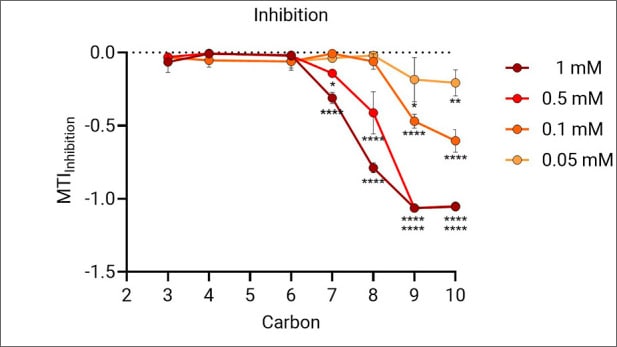
Chain Length-Dependent Mitochondrial Toxicity of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids: Insights from Mito Tox Index Evaluation
This study examines the toxic effects of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs), a PFAS subgroup, on cellular bioenergetics. Using Agilent Seahorse XF Mito Tox assays with the Agilent Seahorse XF Pro analyzer and impedance-based viability analysis (Agilent xCELLigence RTCA), the findings reveal that PFCAs cause chain length–dependent mitochondrial dysfunction, primarily through proton leak–mediated electron transport chain uncoupling. This results in bioenergetic collapse, impaired energy production, and cytotoxicity.
Figure adapted under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. from Kam Y et al. 2025.

Assessing Water Cytotoxicity with an Impedance-Based, Real-Time, and Label-Free Cellular Assay
In this application note, the Alberta Centre for Toxicology employed the Agilent xCELLigence RTCA MP system to conduct noninvasive, label-free, real-time impedance-based monitoring of cellular growth dynamics following exposure to cumulative toxicants present in environmental water samples. This in vitro cell-based assay facilitates quantitative assessment of cytotoxicity through impedance-derived metrics, including the Water Toxicity Index (WTI), Percentage of Biological Effect (PoE), and cell growth inhibition. Moreover, the platform offers high-throughput screening capabilities for systematic surveillance of water quality and identification of potential environmental risk hotspots.

Detection of Bacteria in Environmental Waters using the NovoCyte Flow Cytometer
In this application note, the Agilent NovoCyte flow cytometer was employed as a highly sensitive and efficient platform for detecting and characterizing microbial populations in water samples from diverse sources. The analysis encompassed parameters such as cell size, abundance, nucleic acid content, and bacteria classification, independent of microbial cultivability, typically required in the conventional approach. This method enables precise and rapid quantification of bulk microbial characteristics while providing detailed information on the general microbial state.

Utility of Variable Bandwidth Monochromators for Quantification of Fluorescent Probes in Produced Effluent Water
This application note demonstrates how variable bandwidth monochromators in Agilent BioTek microplate readers optimize detection of fluorescent probes for monitoring trace pollutants in produced effluent water. By tuning excitation and emission wavelengths and bandwidths, researchers can achieve exceptionally low limits of detection—down to parts per trillion—while minimizing background interference. The approach supports simultaneous analysis of multiple probes, enabling sensitive, high-throughput quantification without harmful solvents or complex workflows. These capabilities simplify environmental monitoring and deliver robust, reproducible results that exceed regulatory requirements for pollutant detection.
Tek Tips
Combine Chemical Analysis with Automated Cellular Bioassays for High-Throughput Environmental Testing
Chemical assays tell you what is present; cellular assays reveal what it does. By combining these two strategies—and leveraging automation—environmental testing programs can move beyond detection to impact assessment. For example:
- Start with chemical profiling to identify contaminants and quantify concentrations.
- Add automated cell-based functional assays—such as label-free real-time impedance monitoring or kinetic imaging—to measure cytotoxicity and stress responses in living cells.
- Incorporate specialized bioassays like γH2AX for genotoxicity or Seahorse XF for mitochondrial function to uncover mechanisms of action.
- Use high-throughput platforms and integrated analysis software to streamline workflows, reduce variability, and accelerate decision-making.
This integrated approach provides a fuller picture of environmental risk, enabling researchers to prioritize remediation strategies and regulatory decisions based on both chemical presence and biological effect—at scale.
Key Experimental Considerations for Cell-Based Assays in Environmental Toxicology
When designing cell-based assays to investigate environmental toxicants, consider the following critical experimental conditions:
- Acute versus long-term exposure: Acute exposure (hours to a few days) can reveal immediate cellular stress responses, while long-term exposure (days to weeks) is critical for understanding adaptive mechanisms or chronic toxicity. However, to mimic cumulative effects over extended periods, higher-than-environmental concentrations may sometimes be necessary.
- Concentration-response design: High concentrations may mimic contamination events but can cause nonphysiological stress or cell death. Lower, environmentally relevant concentrations are essential for chronic exposure studies to avoid artifacts. Including a gradient of concentrations can help identify thresholds for toxicity and metabolic disruption. Consider using logarithmic dilution series for broad coverage.
- Account for bioavailability: Some pollutants bind to media components or degrade over time, so verify actual exposure levels using analytical methods or refresh media containing pollutant periodically.
- Water exposure without osmotic stress: When studying pollutants in water samples, avoid replacing culture media with pure water, as this can cause osmotic shock and cell lysis. Instead, consider preparing concentrated pollutant stocks from samples or consider the saline concentration in the water sample and adjust accordingly to maintain cells' integrity.
Product Spotlights
Seahorse XF Pro Analyzer
The Agilent Seahorse XF Pro analyzer delivers unparalleled insights into cellular bioenergetics for environmental research. By simultaneously quantifying mitochondrial respiration and glycolytic activity in real time, Seahorse XF Pro provides a comprehensive metabolic profile that reveals how environmental stressors impact energy production and cellular health and deeper information about mechanisms of toxicity and metabolic adaptation.

BioTek Cytation Cell Imaging Multimode Readers
With integrated multimode detection and automated digital microscopy, the Agilent BioTek Cytation delivers a streamlined workflow for environmental analysis and pollutant detection. Its robust variable bandwidth monochromator provides exceptional sensitivity for precise spectral scanning and optimization of novel fluorescent probes, ensuring maximum signal-to-noise ratio for accurate trace quantification. In addition, the system’s flexible automated imaging capabilities and powerful integrated image analysis tools enable high-content evaluation of cellular responses, supporting both routine measurements and advanced studies, all while accelerating higher-throughput applications.
Novocyte Flow Cytometers
Agilent flow cytometers deliver high-resolution, high-sensitivity data for environmental monitoring and water quality analysis. The NovoCyte series offers flexible configurations—from systems with up to five lasers and 73 detectors to models optimized for detecting low-abundance microorganisms. Paired with NovoExpress software and automated sampling options, Agilent solutions streamline acquisition, analysis, and reporting—saving time and improving reproducibility for microbial detection, contaminant analysis, and other critical water quality assays.


xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analysis Systems
Agilent xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analysis (RTCA) systems use noninvasive biosensor technology to provide continuous, quantitative monitoring of cell health and behavior—ideal for environmental and water quality applications. This platform enables real-time assessment of processes such as chemical- and contaminant-induced cytotoxicity, with minimal hands-on effort. By delivering highly sensitive kinetic data, xCELLigence RTCA surpasses traditional endpoint assays, offering deeper insights into dynamic cellular responses to pollutants and pathogens.
Webinar
Investigating Energy Metabolism Dysfunction in the Tox Space
In this webinar Dr. Jia Shenglan, research fellow from the Nanyang Environment & Water Research Institute (NEWRI) in Singapore, will discuss the investigation of toxicity effects and mechanisms underlying energy metabolism and dysregulation in the environmental toxicology space.
A novel cell analysis workflow featuring analysis of cellular bioenergetics using the Agilent Seahorse XFe96 and real-time oxidative stress assays using the xCELLigence RTCA eSight will be explored.

Additional Resources
Application & Industries
Application Notes
- Automated Imaging and Dual‑Mask Spot Counting of γH2AX Foci to Determine DNA Damage on an Individual Cell Basis
- Automated Comet Assay Imaging and Dual-Mask Analysis to Determine DNA Damage on an Individual Comet Basis
- Advanced Analysis of Aquatic Plankton using Flow Cytometry
- A Customized XF Workflow for Detection and Characterization of Mitochondrial Toxicity
- Monitoring Bacterial Growth under Different Environmental Conditions
News
Upcoming Conference
SOT 65th Annual Meeting and ToxExpo
March 22-25, 2026 | San Diego, CA