Access Agilent eNewsletter November 2016

Fast, accurate analysis of SVOCs with Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC
Matthew Giardina, Ph.D., Agilent Applications Chemist
The combination of gas chromatography and mass spectrometry is widely deployed for the analysis of semivolatile organic compounds (SVOCs) in environmental samples. A substantial number of SVOCs are considered to be environmental pollutants. USEPA method 8270D identifies a list of 243 compounds that are suitable for analysis by GC/MS in solid waste, soil, air, and water extracts.
The durability and data quality of the Agilent 7890 GC has set the global standard for the analysis of SVOCs. The analysis described in this article demonstrates that the Agilent 9000 Intuvo—the next generation of GC instrumentation—easily meets the requirements of USEPA method 8270D.
Agilent 9000 Intuvo takes SVOC analysis to the next level
The Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC includes innovations that make it well suited to SVOC analysis. New flow technology incorporates the easy-to-install/replace Intuvo column and Guard Chip that function as a pre-column to prevent contamination. What’s more, direct heating technology reduces power requirements and facilitates rapid column cooling for faster cycle times.
For this application, a stock standard containing 77 target compounds and surrogates was selected to provide a representative mixture of acids, bases and neutrals. A composite mixture of soils prepared for 8270 contained the heaviest matrix residue typically encountered in a laboratory.
The Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC was configured with a single MS flow path for interfacing to an Agilent 5977 with an inert EI ion source. Table 1 lists the instrument conditions used during the study.
| Injection volume | 1 µL |
| Inlet |
Split/splitless 300 °C Pulsed splitless 60 psi until 0.5 min Purge 50 mL/min at 0.5 min Septum purge switched flow mode 3mL/min |
| Liner | Agilent Ultra Inert splitless single taper liner with glass wool |
| Guard Chip (Intuvo only) | 60 °C for 2 min, 20 °C/min to 260 °C, 6 °C/min to 330 °C hold 1.333 min (standards) or 10.333 min (soil extract) |
| Column | Agilent DB-5ms UI 30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.5 µm |
| Flow | 2 mL/min constant flow |
| Column temperature | 40 °C for 2 min, 20 °C/min to 260 °C, 6 °C/min to 330 °C hold 1.333 min (standards) or 10.333 min (soil extract) |
| Transferline temperature | 330 °C |
| Drawout plate | 6 mm (option) |
| Ion source temperature | 330 °C |
| Quadrupole temperature | 200 °C |
| Scan | 35 to 550 m/z |
| Gain factor | 1 |
| Threshold | 50 |
| A/D samples | 2 |
Table 1. Common GC/MS Parameters
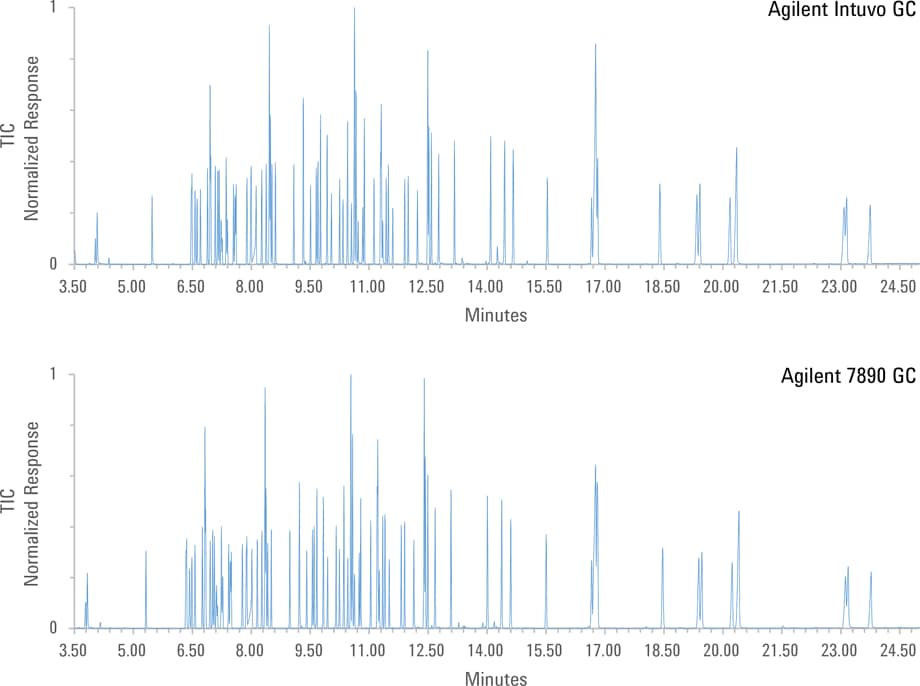
Figure 1. Comparison of SVOC chromatograms generated with the Agilent Intuvo 9000 and 7890.
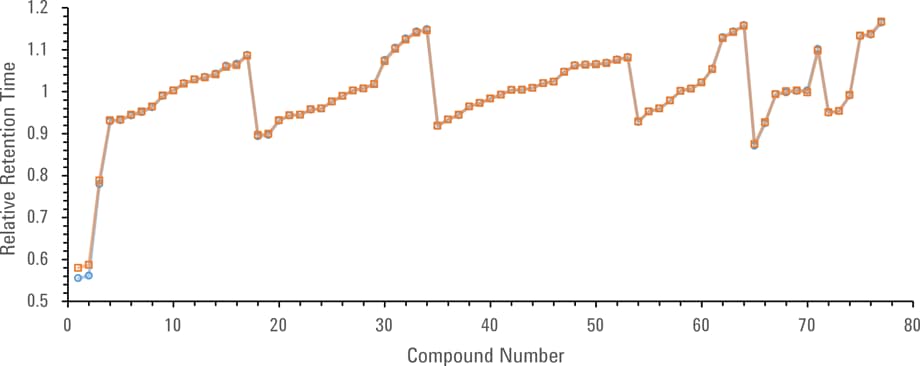
Figure 2. Comparison of relative retention times for SVOCs with Intuvo 9000 (orange squares) and 7890 GC (blue circles).
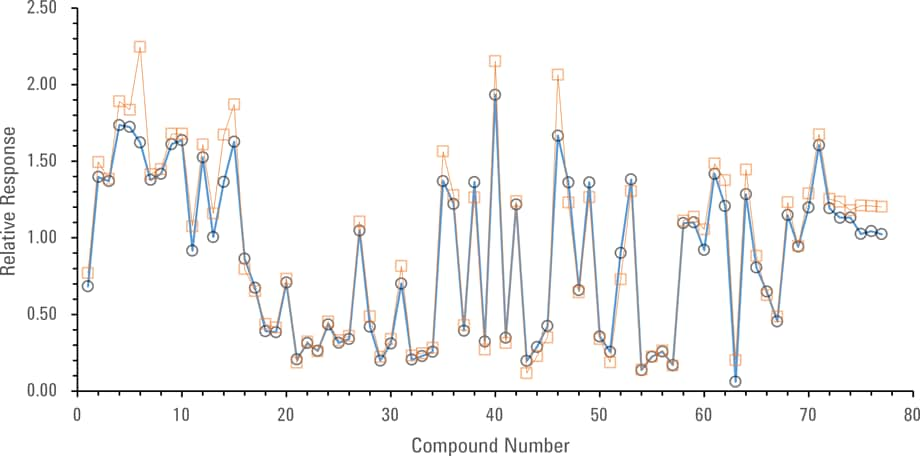
Figure 3. Comparison of relative retention times for SVOCs with the Intuvo (orange squares) and 7890 (blue circles).
Intuvo 9000 meets 7890 performance benchmark
As an initial validation of equivalency, a standard prepared with a target and surrogate concentration of 20 µg/mL and internal standard concentration of 40 µg/mL was injected on an Agilent 7890/5977 and 9000/5977. Figure 1 shows a normalized total ion chromatogram obtained on both systems. The chromatograms are virtually indistinguishable with only slight differences in regions of high peak density (12.5 and 16.5 minutes).
To provide a more quantitative comparison of retention, Figure 2 shows a plot of the relative retention times for the Agilent Intuvo 9000 and 7890 GC systems. The agreement between the two instruments was quite good, with an average 0.0006 difference in relative retention time.
As observed in Figure 2, the first two eluting compounds, N-nitrosodimethylamine and pyridine, show a greater degree of difference in relative retention time. This is a result of a small amount of pre-column volume introduced by the Agilent Intuvo Guard Chip.
Figure 3 shows that the relative responses of the last eluting polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) were slightly greater on the Intuvo 9000 compared to 7890. This demonstrates that the thermal profile across the Agilent Intuvo flow path is consistent, allowing the higher boiling point PAHs to pass through the flow path and maintain recovery and peak shape.
Running a gauntlet of matrix injections
A total of 680 matrix injections were performed. After each interval of 20 sample injections, the matrix load was sufficient to cause almost complete breakdown of 4,4’-DDT. Following the testing protocol, the liner and septum were replaced and the system was retested. After liner replacement, the percent breakdown dropped below 20%.
Based on this experiment, a preventive maintenance cycle can be estimated at one Intuvo Guard Chip replacement after every 60 matrix injections. This replacement frequency would be sufficient for most soil matrices. Additionally, the Guard Chip can be replaced more quickly and easily on the Intuvo 9000 compared to column trimming on the 7890.
Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC is optimized for SVOC analysis
This study demonstrates the suitability of the Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC System for the analysis of SVOCs. The Intuvo 9000 can easily meet the performance requirements as specified by USEPA method 8270D. Compared to the 7890, the Agilent Intuvo 9000 provided equivalent results in terms of relative retention time and relative response. In addition, repetitive injections of a soil extract illustrated the resilience of the Intuvo 9000 to a substantial matrix challenge and the ease of maintenance compared to the 7890 GC system.
Agilent—A rich heritage of gas chromatography innovations
For over 50 years, Agilent has pioneered the technologies that define how gas chromatography is performed today. Beyond its industry-leading analytic solutions, Agilent provides consumables, workflow solutions, and software to ensure success in applications from the routine to the most complex. Contact an Agilent representative today to find out more.
Stay informed about the applications that are important to you
Subscribe to Access Agilent
Our free customized
monthly eNewsletter
Article Directory – November 2016
All articles in this issue
-
 Agilent 7010B and 7000D QQQ GC/MS systems expand your lab in multiple dimensions
Agilent 7010B and 7000D QQQ GC/MS systems expand your lab in multiple dimensions -
 Fast, accurate analysis of SVOCs with Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC
Fast, accurate analysis of SVOCs with Agilent 9000 Intuvo GC -
 Integrated workflow simplifies automated calculation of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR)
Integrated workflow simplifies automated calculation of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) -
 Tips & tricks:
Tips & tricks:
How to simplify troubleshooting in your GC lab using Agilent ADM Flow Meter -
 Agilent collaborates with BioPharma thought leaders in India to advance biosimilar characterization
Agilent collaborates with BioPharma thought leaders in India to advance biosimilar characterization -
 Achieve fast, high throughput size exclusion chromatography of mAbs and ADCs using Agilent AdvanceBio SEC columns
Achieve fast, high throughput size exclusion chromatography of mAbs and ADCs using Agilent AdvanceBio SEC columns -
 Ask the Expert: How can I analyze virtually any polymer, from paints to polyolefins?
Ask the Expert: How can I analyze virtually any polymer, from paints to polyolefins? -
 Agilent LC/MS/MS solutions provide effective identification and quantitation of contaminants in botanical drug supplements
Agilent LC/MS/MS solutions provide effective identification and quantitation of contaminants in botanical drug supplements -
 Agilent JetClean self-cleaning ion source means you clean less, analyze more
Agilent JetClean self-cleaning ion source means you clean less, analyze more -
 High-throughput N-linked glycan profiling of monoclonal antibodies using Agilent integrated solution
High-throughput N-linked glycan profiling of monoclonal antibodies using Agilent integrated solution
Figure 1

Comparison of SVOC chromatograms generated with the Agilent Intuvo 9000 and 7890.
Figure 2

Comparison of relative retention times for SVOCs with Intuvo 9000 (orange squares) and 7890 GC (blue circles).
Figure 3

Comparison of relative retention times for SVOCs with the Intuvo (orange squares) and 7890 (blue circles).