Access Agilent eNewsletter, July 2014
>> Update My Profile | Subscribe to Access Agilent | Article Directory

New Agilent HILIC column delivers improved resolution and high speed analysis of N-linked glycans
By James Martosella
Agilent Bio-applications
The largest group of therapeutic proteins is made from recombinant monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). To be effective, mAbs must have the correct glycosylation pattern. Human mAbs have a single conserved N-linked glycosylation site on each heavy chain.N-linked glycosylation is a critically important and very complex post-translational modification. It; therefore, needs to be controlled and monitored throughout the development, processing, and manufacture of drug glycoproteins.
Therapeutic protein characteristics, including safety, efficacy, and serum half-life, can be affected by differences in their glycosylation pattern, and so the analysis of these patterns is an important part of the characterization of therapeutic glycoproteins, particularly mAbs.
Glycans are best described more generally as branched oligosaccharides. Different strategies have been applied for their analysis. However, the majority of methods are based on enzymatic protein release of glycans from the mAb, with subsequent derivatization with a labeling agent, such as 2-aminobenzamide (2-AB). Due to the lack of chromophores on the glycan, labeling with a 2-AB (neutral) tag enables fluorescence detection. Labeled glycans are very hydrophilic structures and the preferred separation technique is by hydrophilic interaction chromatography, commonly referred to as HILIC. Separation using HILIC with fluorescence detection is a robust method for glycan analysis, whereas HILIC/LC can also be coupled to mass spectrometry to obtain important mass and structure information.
Speed counts
One of the growing challenges in HILIC/LC, however, is achieving high resolution separations with fast analysis times. With ever increasing demands placed on biocharacterizations for higher throughput, researchers are looking for improved separation (HILIC) methods, but not at the cost of lost separation performance. Since glycans include many closely related structures, it is critical to achieve the highest resolution possible, and preferably during a fast analysis time.
 Enlarge
Enlarge
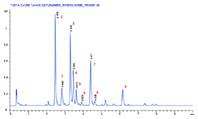
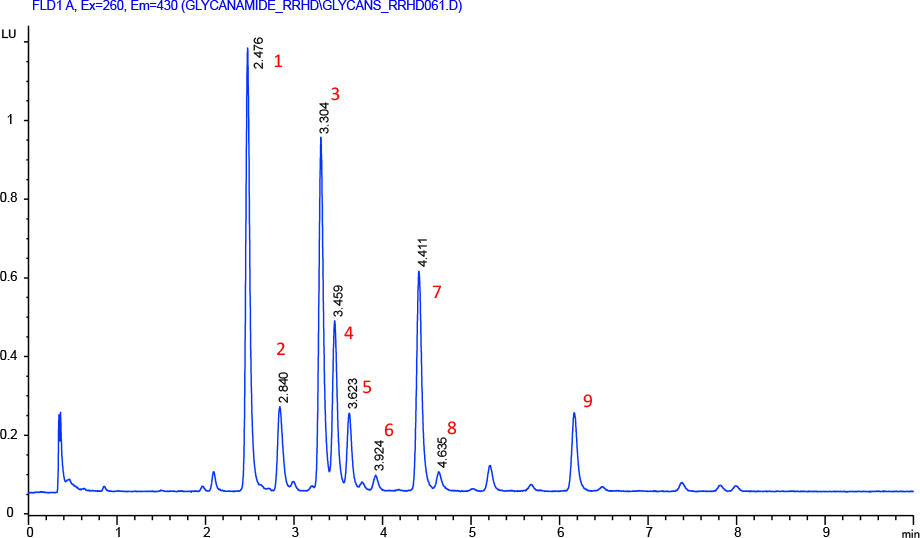
Figure 1. Separation of 2-AB labeled N-linked human IgG glycans on an Agilent AdvanceBio Glycan Mapping column.
To tackle these separations, Agilent has introduced the AdvanceBio Glycan Mapping column that delivers high resolution separations of glycans. The Agilent AdvanceBio Glycan Mapping column is based on a 1.8 µm totally porous particle with novel amide-bonded phase chemistry. This column has high resolution capability for separating glycan structures, providing high compatibility with common HILIC mobile phases and operating conditions. It also has been optimized for routine use with UHPLC/MS and fluorescence detection to achieve reproducible and reliable rapid separation of glycans, especially mAb-generated glycans.
To demonstrate this separation performance, a 2.1 x 150 mm Agilent AdvanceBio Glycan Mapping column was used to profile human mAb glycans. In Figure 1, 2-AB labeled glycans from a human IgG were separated using HILIC. Separations were monitored by fluorescence and MS detection. In this separation, the labeled glycans are highly resolved, displaying excellent peak shapes and high sensitivity. The column delivered steady baseline performance and narrow peak widths to enable the accurate detection of close eluting peaks. The glycan column, coupled to an ESI-QTOF MS instrument, provided accurate glycan assignment for peaks 1 to 9 (Table 1). This demonstrates the column’s unique ability to rapidly and efficiently profile human mAb glycans for biotherapeutic characterizations.
# |
Glycan identification |
Structure |
|---|---|---|
1 |
G0F /FA2 |
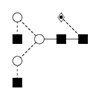 |
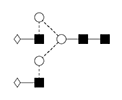
2 |
G0FB/FA2B |
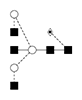 |
3 |
NA2G1F/ 1,6 G1F/F(6)A2[6]G(4)1 |
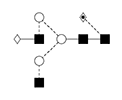 |
4 |
NA2G1F/ 1,3 G1F /F(6)A2[3]G(4)1 |
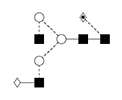 |
5 |
G1FB/ FA2BG1 |
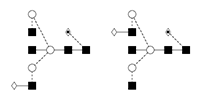 |
6 |
G2/A2G2 |
 |
7 |
G2F/FA2G2 |
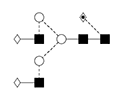 |
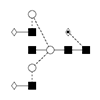
8 |
G2FB/FA2G2B |
 |
9 |
A1F/FA2G2S1 |
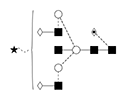 |
Table 1. Peak number, glycan identity and structure.
Improving workflows even more
Traditionally, N-glycan sample preparation has been a labor-intensive, low-throughput process taking several days. The Agilent AssayMAP N-Glycan Sample Preparation system now uses ProZyme solutions for N-glycan sample prep, delivering an automated, highly robust, high-throughput process that requires little hands-on time. Samples are ready for analysis in hours, not days.
The Agilent AdvanceBio Glycan Mapping column and Agilent AssayMAP are just two of Agilent’s comprehensive portfolio of solutions for confirmation of protein sequence, identification of modifications, and routine protein fingerprint monitoring. Go to Accurate Solutions for Protein Characterization and explore the whole family.
>> Update My Profile | Subscribe to Access Agilent | Article Directory
Figure 1.
column |
Avg. RT (min) |
RS 2,1 |
RS 3,2 |
R S4,3 |
RS 6,5 |
avg. PW (min) |
Peak Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Glycan Mapping |
3.93 |
1.63 |
1.70 |
3.05 |
2.09 |
0.059 |
135 |
Conditions |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Flow rate |
1.00 mL/min |
|||||||||
Temperature |
55 °C |
|||||||||
Injection volume |
2 µL 70:30 CAN:water |
|||||||||
Eluent |
A, 100 mM NH4Fc, pH 4.5; B, ACN |
|||||||||
Gradient |
|
|||||||||
Excitation |
260 nm |
|||||||||
Emission |
430 nm |
|||||||||
Sample |
ProZyme human IgG glycan library |
|||||||||
Separation of 2-AB labeled N-linked human IgG glycans on an Agilent AdvanceBio Glycan Mapping column.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.